Apnea Detection with AnisotropicResNet
This project focuses on detecting sleep apnea episodes from tracheal sound recordings using deep learning. The AnisotropicResNet model is designed to process audio features such as Mel Spectrogram, MFCC, and Chroma Features extracted from tracheal sound data. The objective is to accurately predict periods of apnea by leveraging advanced feature extraction and a customized convolutional neural network architecture.
Model Architecture
Model Diagram:
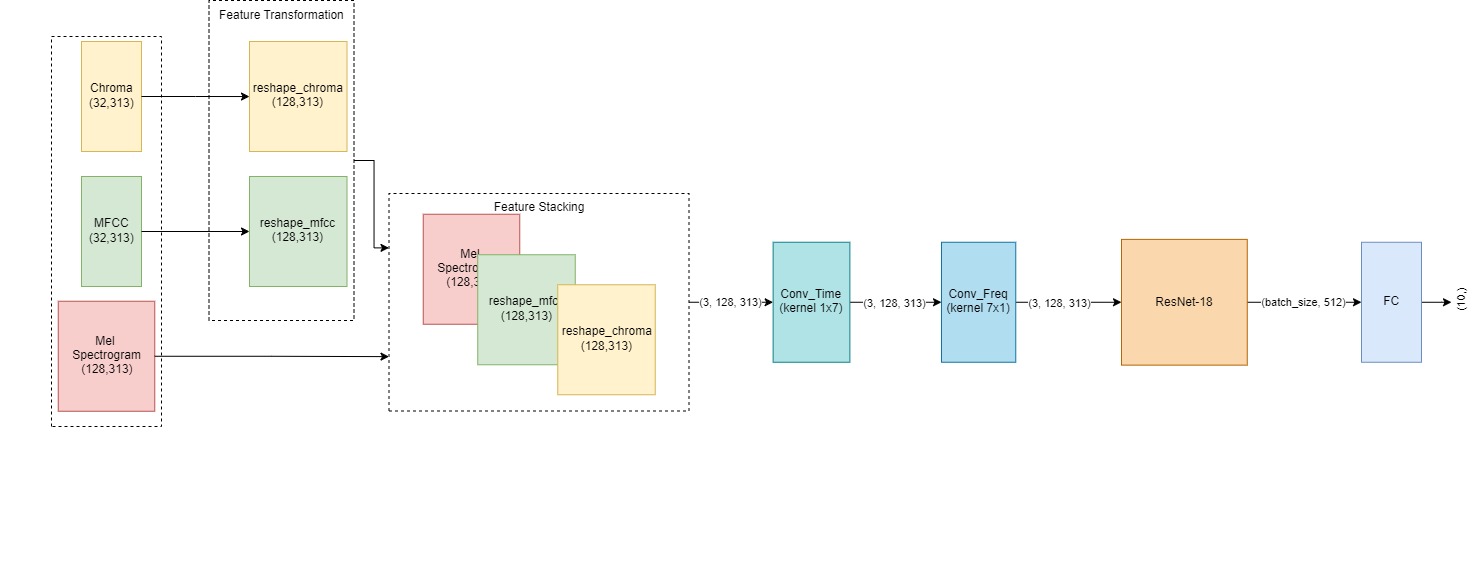
AnisotropicResNet
The AnisotropicResNet model is a modified version of the ResNet-18 architecture, specifically tailored for the task of apnea detection. The model combines multiple audio features to form a 3-channel input, enabling the network to simultaneously process temporal and frequency information from the audio signals.
-
Input:
- The model takes three key audio features as input:
- Mel Spectrogram: A visual representation of the power spectrum of audio signals on the mel scale.
- MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients): Captures short-term power spectrum of sound, frequently used in speech recognition.
- Chroma Features: Represents the energy distribution across 12 pitch classes (chromas), useful for capturing harmonic content.
- The model takes three key audio features as input:
-
Feature Reshaping:
- To unify the dimensions of the input features, two fully connected layers are applied to reshape the MFCC and Chroma Features to match the size of the Mel Spectrogram. These reshaped features are then stacked to form a 3-channel input image.
-
Convolutional Layers:
- The model applies two initial convolutional layers:
- Temporal Convolution (1x7 kernel): Focuses on capturing patterns along the time axis.
- Frequency Convolution (7x1 kernel): Captures frequency patterns from the audio data.
- The model applies two initial convolutional layers:
-
ResNet Backbone:
- The modified ResNet-18 architecture processes the stacked 3-channel input, learning deep features from the combination of Mel Spectrogram, MFCC, and Chroma.
-
Output:
- The final output layer generates predictions for apnea episodes based on the given time windows, leveraging the deep features learned by the network.
Results
The model was trained and evaluated on real tracheal sound data with various patients. The primary evaluation metrics include Precision, Recall, and F1 Score, which measure the accuracy of predicting apnea episodes. The model performance was analyzed both quantitatively and qualitatively, showing that it is capable of identifying apnea regions with a high degree of accuracy.
Explanation of True Positive (TP):
A True Positive (TP) refers to a situation where the predicted apnea region has an Intersection over Union (IOU) greater than 70% with the actual ground truth apnea region. This threshold ensures that the predicted region significantly overlaps with the true apnea region, making it a valid and accurate prediction.
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 10 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.89 | 6.5 |
| Model 2 | 0.8 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 4.25 |
| Model 7 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 4.0 |
| Model 5 | 0.67 | 0.6 | 0.63 | 3.17 |
| Model 4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.58 | 6.14 |